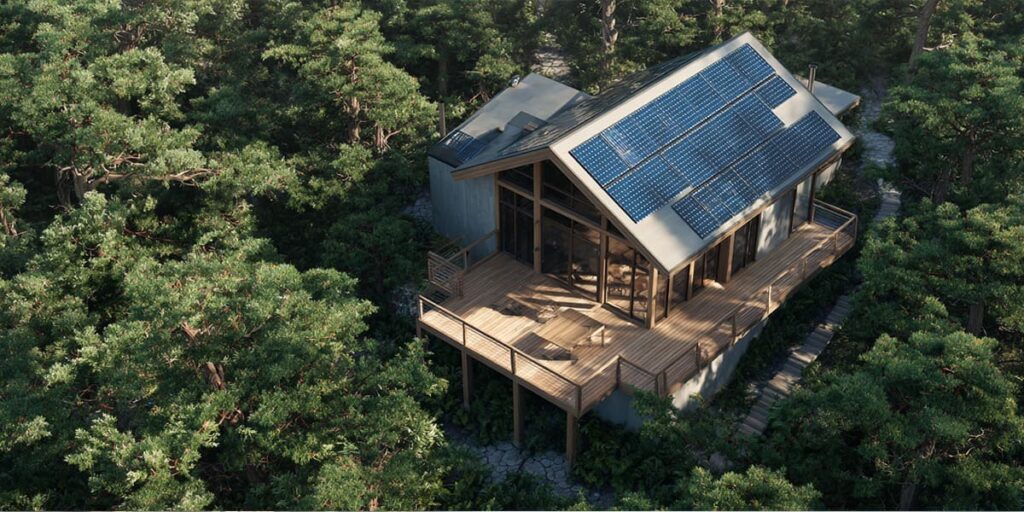
The idea of escaping the grid is no longer just a wilderness fantasy. Across India, a quiet shift is underway, one where homebuyers are beginning to see off-grid homes and semi-remote living not as isolation, but as independence. Once limited to eco-retreats and weekend cottages, this movement is now entering mainstream residential planning through sustainable homes, renewable energy integration, and green real estate innovations that promise autonomy without compromise.
But is off-grid living truly the future, or just another passing trend in India’s evolving housing market?
A Global Movement Finds Indian Ground
Globally, off-grid housing has become a legitimate real-estate segment. In countries like the US, Australia, and parts of Europe, eco-friendly houses powered by solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and composting systems have moved from niche to norm in certain regions.
India is catching up fast. Driven by rising energy costs, water scarcity, and environmental awareness, more buyers now view self-sufficiency as both practical and aspirational. The
demand is not only for off-grid homes in India, but also for remote homes that remain connected digitally while functioning sustainably.
Developers are responding. Projects on the outskirts of cities like Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and Pune now incorporate solar microgrids, on-site wastewater recycling, and passive ventilation systems. The goal is to balance comfort with conservation, an equation that defines the next phase of green real estate.
Why the Shift Is Happening Now?
Three broad drivers are pushing this change from concept to reality.
1. Climate Responsibility Becomes Personal
With rising awareness around carbon footprints, urban homebuyers increasingly view sustainability as a lifestyle choice. The 2024–25 Global Sustainability Index noted that over 60% of urban Indians would pay a premium for eco-friendly houses that reduce energy dependence and water waste.
What was once a developer’s differentiator is now becoming a buyer’s baseline expectation.
2. Infrastructure Expands Beyond City Cores
Thanks to stronger digital networks, expressways, and renewable energy infrastructure, living semi-remote no longer means living disconnected. Regions that were once considered “outside the city”, places like Tukkuguda near Hyderabad or Nandi Hills near Bengaluru, now offer excellent accessibility while enabling off-grid homes to operate efficiently with solar, biogas, and local water management.
3. Technology Makes Sustainability Convenient
Today’s sustainable homes integrate smart systems that monitor energy use, manage battery storage, and automate irrigation. Advances in energy-efficient construction materials and IoT-enabled devices mean eco-living no longer feels like compromise. In essence, technology has turned sustainability into comfort.
The New Vocabulary of Independence
For many urban families, the idea of an off-grid home represents freedom, from power outages, unpredictable utility bills, and environmental guilt. But it also represents something deeper: a return to balance between built and natural environments.
Developers designing remote homes are exploring layouts that maximise daylight, ventilation, and rain capture. Materials such as lime plaster, terracotta, and reclaimed wood are replacing high-carbon alternatives. Even wastewater is seen as a resource, not waste.
This isn’t a minimalist retreat lifestyle; it’s a recalibrated one, one that blends smart urban sensibility with ecological mindfulness.
The Economics Behind Green Real Estate
There’s a misconception that green real estate costs significantly more. While upfront investment in renewable systems or sustainable materials can be higher, lifecycle costs tell a different story.
Studies by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) show that eco-friendly houses consume 20–30% less energy and 35–40% less water than conventional homes, translating into long-term operational savings. Similarly, government incentives for solar installations, rainwater harvesting, and on-site composting are further improving the return profile of off-grid homes in India.
From an investor perspective, properties with sustainability certifications are already commanding 8–10% higher resale value in major metros. The market is rewarding responsibility.
The Indian Context: Semi-Remote, Not Isolated
Full off-grid living, completely independent from civic utilities, remains rare in India’s dense urban framework. What’s emerging instead is the hybrid model: semi-remote homes within planned communities that generate part of their own power, harvest water, and manage waste on-site while staying digitally and logistically connected.
Projects near Hyderabad’s outer ring, for example, are pioneering this balance. These developments cater to buyers seeking wellness-oriented, nature-linked lifestyles without disconnecting from city access. They represent what might be called “connected isolation”, privacy with proximity, sustainability with structure.
Will the Trend Last?
The sustainability conversation in Indian housing is no longer symbolic. With climate conditions worsening and resource costs climbing, sustainable homes have shifted from being lifestyle statements to future-proof necessities.
However, the permanence of this movement will depend on how responsibly developers execute it. True off-grid homes need long-term planning, not just solar panels or bamboo façades, but full integration of environmental design and urban foresight.
If implemented thoughtfully, this is not a fad. It is the natural progression of a maturing real-estate ecosystem that recognises that luxury and responsibility are no longer opposites.
The Future Is Designed to Sustain
As India urbanises, off-grid homes in India may become key to decentralising pressure on city grids. Semi-remote living will enable communities to grow around natural resources rather than deplete them.
For forward-thinking developers, this shift presents not a challenge but an opportunity, to build eco-friendly houses that reflect the intelligence of design and the conscience of a generation seeking balance.
Whether it’s power, water, or peace of mind, the future of housing lies not in consumption, but in regeneration.
And that makes green real estate not a passing trend, but the blueprint of how we’ll truly live tomorrow.
Navanaami: Advancing the Practice of Sustainable Design
At Navanaami, sustainability functions as a design principle rather than a decorative idea. Each project integrates measurable performance in energy efficiency, water use, and indoor well-being. This results in eco-friendly houses and sustainable homes that align with both environmental priorities and everyday comfort.
The developments created under Navanaami’s portfolio reflect the next phase of green real estate in India. They demonstrate how communities can be technologically advanced, yet environmentally balanced. The emphasis remains on systems that replenish, materials that endure, and spaces that support the health of their occupants.
Navanaami views sustainability as a practice that evolves with research, design, and accountability. It is not adopted for appeal; it is applied for permanence.
FAQs
1. What are off-grid homes and why are they gaining popularity in India?
Off-grid homes are self-sustaining houses that operate independently of public utilities through solar power, rainwater harvesting, and on-site waste management. In India, these eco-friendly houses are becoming popular as more homebuyers seek energy independence, water security, and a reduced carbon footprint.
2. How do off grid homes in India work?
Most off grid homes in India use solar panels for electricity, borewells or rainwater systems for water, and organic waste composting for sustainability. These homes blend renewable energy and smart design to achieve year-round self-reliance, making them benchmarks for sustainable homes and green real estate.
3. Are off grid homes suitable for urban buyers or only for remote locations?
While originally built in rural areas, off grid homes are now entering city outskirts as part of green real estate developments. Many urban buyers are choosing semi-remote or hybrid sustainable homes that remain connected digitally but independent in resource management, balancing convenience with sustainability.
4. What are the main advantages of living in an eco-friendly house?
Eco-friendly houses offer lower utility bills, improved air quality, and long-term energy savings. By using solar energy, recycled water, and natural materials, these homes reduce environmental impact while creating healthier living spaces, the core principle of sustainable homes and green real estate design.
5. How is green real estate shaping India’s housing market in 2025?
In 2025, green real estate is shifting from niche to mainstream. Developers are integrating solar rooftops, wastewater recycling, and passive cooling to create sustainable homes that appeal to conscious buyers. This evolution marks India’s move toward a more climate-resilient and responsible housing model.
6. What’s the difference between off-grid and semi-remote homes?
Off-grid homes operate fully independent of municipal systems, while semi-remote homes generate partial power and water but stay connected to city infrastructure. Both models reflect the growing trend of eco-friendly houses designed to reduce dependence on traditional grids without sacrificing comfort.
7. Are off grid homes in India expensive to build or maintain?
While initial setup for off grid homes in India can cost more due to solar panels or rainwater systems, the long-term savings are significant. These sustainable homes lower electricity and water bills, offering excellent lifecycle value for buyers seeking cost-efficient green real estate.
8. Can remote homes still have modern amenities and internet connectivity?
Yes. Today’s remote homes are equipped with high-speed internet, solar-powered appliances, and smart energy management systems. Thanks to improved digital infrastructure, sustainable homes in semi-remote areas now offer modern comfort while staying environmentally responsible.
9. Where are the best locations to buy off grid homes in India?
Popular regions for off grid homes in India include the outskirts of Hyderabad, Bengaluru, Pune, and Goa. These areas provide access to renewable energy sources and strong connectivity, making them ideal for building eco-friendly houses and investing in long-term green real estate.
10. Is off-grid living in India a long-term lifestyle or a short-term trend?
Off-grid and semi-remote living are evolving into long-term lifestyle choices rather than passing trends. With rising environmental awareness and government focus on renewable energy, sustainable homes and green real estate represent the future of responsible housing in India.